
Understanding xSPI: The Future of High-Speed Flash Memory Interfaces
Introduction to XSPI (What is XSPI?)
xSPI stands for “eXpanded Serial Peripheral Interface”. It’s a high-speed communication protocol designed to interface with NOR flash memory and other peripherals. xSPI is an enhanced version of the standard SPI, offering faster data transfer speeds and greater efficiency. xSPI supports multiple data lanes, which enables faster read and write speeds compared to the traditional SPI protocol. It is standardized under JEDEC JESD251 and JESD251-1.
Visuals:
Block diagram of xSPI Host (controller) connected to flash memory (Target) with arrows showing Clock, Chip select and multiple data lanes,
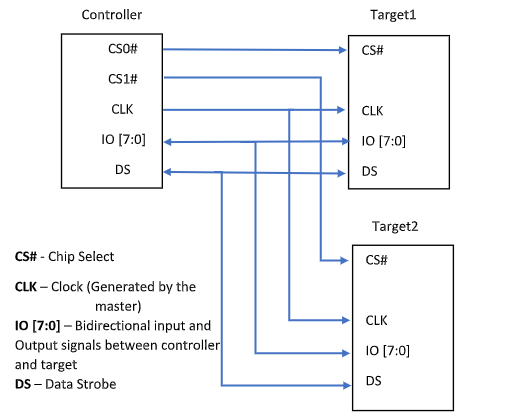
Why is xSPI important?
- The increasing demand for faster data processing, such as in embedded systems, IoT (Internet of Things) and automotive electronics products has made xSPI crucial. It provides significant improvements in memory access speed, enabling faster boot times, quicker data retrieval, and overall enhanced system performance.
High-Speed Data Transfer
- Supports Octal SPI (8-bit wide) for faster communication.
- Offers speeds up to 400 MB/s or more with DDR (Double Data Rate) mode.
Improved System Performance
- Reduces boot time for embedded systems.
- Efficient memory-mapped read access for processors, enabling seamless execution of code from external flash.
Standardization and Interoperability
- Ensures compatibility across different flash memory vendors.
- Simplifies the integration process for system designers.
Low Power Consumption
- Optimized for battery-powered applications like IoT devices, automotive systems, and mobile devices.
Advanced Features
- Error Correction Code (ECC) for improved data integrity.
- Security features like authentication and encryption for secure boot and firmware updates.
What is the advantages of xSPI over QSPI
- Faster Data Transfer
xSPI supports more data lanes than QSPI, which allows it to transfer data at higher speeds. This results in faster performance for systems that need quick data access. - Lower Latency
XSPI reduces delays in data transmission, making it ideal for real-time applications where every millisecond counts, such as in automotive and industrial systems. - Greater Scalability
xSPI can handle multiple lanes and is more flexible, allowing it to support higher speeds as technology advances, making it future-proof for growing data needs. - Better Performance in Complex Systems xSPI is better suited for high-performance applications, such as high-resolution video or advanced sensors, where large amounts of data need to be processed quickly.
- Improved Efficiency
xSPI reduces bottlenecks in data transfer, allowing the system to operate more efficiently, leading to smoother performance in demanding environments. - Comparison of Traditional SPI, QSPI and xSPI
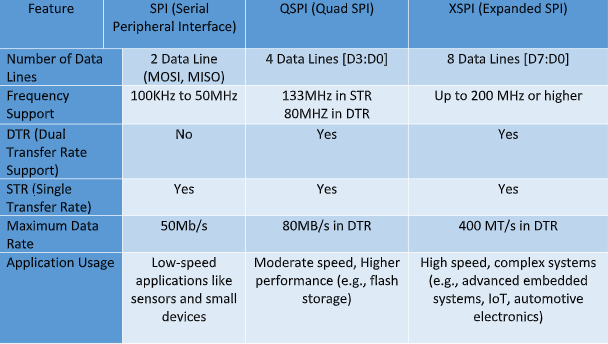
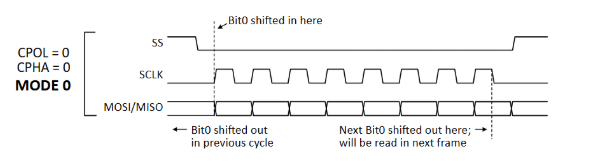
Frame format of SPI, QSPI and xSPI
SPI
QSPI
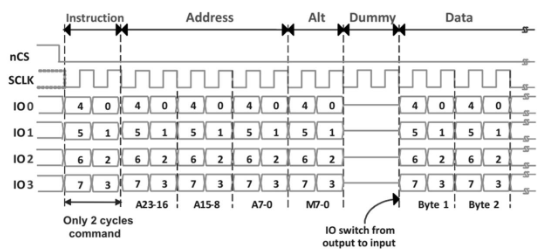
xSPI
1S-1S-1S Mode
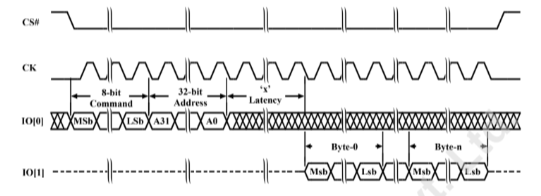
8D-8D-8D Mode
Applications of xSPI
- Automotive Electronics (ADAS, Infotainment, ECU firmware storage)
Industrial Automation (real-time controllers, PLCs) - Aerospace & Defence (secure and high-reliability memory solutions)
- Embedded Systems (MCUs, FPGAs, and SoCs requiring fast external memory access)
Looking to analyze and debug xSPI interfaces efficiently? The PGY-STG-PA XSPI Protocol Exerciser & Analyzer offers comprehensive testing capabilities with:
✔ Support for xSPI/OSPI Protocols
✔ Switching between 1SDR, 8SDR & 8DDR modes
✔ Single, Dual, Quad & Octal SPI compatibility
✔ 8GB DDR memory for deep data analysis
✔ Up to 8 IF-ELSE trigger levels for precise event capture
Explore how PGY-STG-PA can streamline your testing process. Learn more: https://www.prodigytechno.com/xspi-protocol-analyzer



